What is a
resistor?
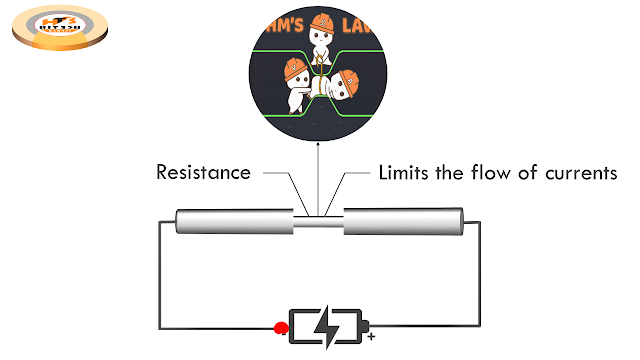
Resistors are passive electrical components
that limit electric current.
Resistor is a passive
electrical component. Its primary function is to limit the flow of electric
current.
To
understand the function and working of resistors, let us consider an uniform
hollow pipe with water flowing through it. If the two similar pipes are now
joined with a narrow pipe relatedly having less diameter or cross-sectional
area. Then the water current will be resisted by the pipe having less
cross-sectional area. It means this particular section of pipe will act as a
resistor for water current. Similarly, a resistor by limiting or reducing the
flow of charge carrier, reduces the flow of electric current in a circuit.
What is OHM’S Law?
Voltage across a resistor
is directly proportional to the current passing through it.
Vµ I
or,
V=R.I
Where, R is a
proportionality constant, it is called resistance of a resistor.
It means that if the
current through a resistance is required to increase, the value of potential
difference or applied voltage across the resistor is required to increase.
Example: To use a LED
(Imax =1 mA, RLED »
0Ω), without damage, in series with a voltage source of 9 Volt, find out the
minimum resistance value of a resistor required to connect in series with the
power supply.
Solution :
As per Ohm’s Law V=R.I
For Imax =1
mA, current ‘I’ should be less than or equals to 1 mA, i.e.
I ≤ 1 mA
V= 9 V
Rmin ≥ V/I,
Rmin ≥ 9Volt/1mA ≥ 9 . 103 Ω
≥ 9kΩ
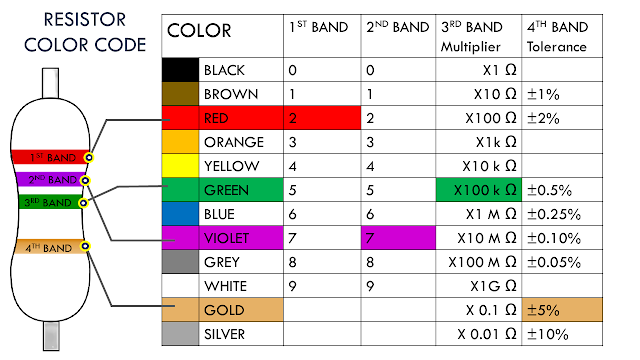
Types of Resistors:
1. Linear
Resistors
a) Fixed
Resistors
i.
Carbon Composition Resistors
ii.
Wire Wound Resistors
iii.
Thin Film Resistors
A. Carbon
Film
B.
Metal Film
iv.
Thick Film Resistors
A. Fusible
Resistors
B.
Metal Oxide Resistor
C. Cermet
Resistors
b) Variable
Resistors
i.
Potentiometer
ii.
Rheostats
iii.
Trimmer
2. Non-Linear
Resistors
a) Photo
Resistors or Light Dependent Resistors
b) Thermistors
c) Varistors
d) SMD
Resistors
1. Linear Resistors: Linear Resistors are those resistors, which current values changes with the change in applied voltage. In other words, we can say that a resistor, which current value is directly proportional to the applied voltage is known as linear resistors. Linear resistors are Ohmic devices and follows the Ohm’s law.
2. Non-Linear
Resistors: Non-Linear Resistors are those resistors, which current
values does not change with the Ohm’s Law. In case of Non-Linear Resistors, the
current value changes with change in applied temperature, light intensity
falling on it. Non-Linear resistors are Non-Ohmic devices and do not follow the
Ohm’s law.















Comments
Post a Comment